Added Sugars and Additives in Corn Flakes

Nutrition facts for corn flakes – Corn flakes, a breakfast staple for many, often contain significant amounts of added sugars and various additives. Understanding the types and quantities of these ingredients is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section will examine the sugar content in popular brands and detail common additives, along with their potential health implications.
Sugar Content in Corn Flakes
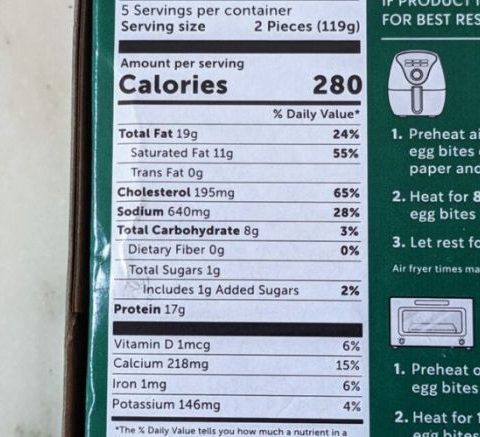
The sugar content in corn flakes varies considerably among brands. Manufacturers often add sugar to enhance flavor and improve texture. This added sugar contributes to the overall calorie count and can impact blood sugar levels. The following table illustrates the sugar content per serving (typically one cup) for several popular brands. Note that these values can fluctuate slightly depending on the specific product batch and serving size.
| Brand | Sugar Content (grams per serving) |
|---|---|
| Kellogg’s Corn Flakes | 3 |
| Post Honeycomb | 11 |
| General Mills Cheerios (original) | 1 |
| Nature’s Path Organic Corn Flakes | 1 |
Common Food Additives in Corn Flakes
Several additives are commonly found in corn flakes to enhance shelf life, texture, and appearance. While generally considered safe in the amounts used, excessive consumption of certain additives has been linked to potential health concerns.
Understanding nutrition facts is crucial for mindful eating. A simple breakfast like corn flakes offers a quick source of carbohydrates, but its nutritional profile is relatively basic. For a broader perspective on nutritional content in processed foods, consider comparing it to the detailed breakdown found in resources like karl strauss nutrition facts , which highlights the complexities of nutritional analysis.
Returning to corn flakes, remember to supplement them with fruits and other nutrient-rich foods for a balanced and healthy meal.
The following are some common additives and their purposes:
- Salt (Sodium Chloride): Enhances flavor and acts as a preservative.
- Maltodextrin: A carbohydrate used as a thickener and sweetener.
- Modified Food Starch: Improves texture and prevents clumping.
- Soy Lecithin: An emulsifier that helps prevent oil separation.
- Artificial Colors (e.g., Yellow 5, Yellow 6): Enhance visual appeal.
- Artificial Flavors: Enhance the overall flavor profile.
- Vitamin and Mineral Fortification: Often added to enhance nutritional value (e.g., iron, B vitamins).
Potential Health Implications of High Sugar and Additive Consumption
High sugar intake from corn flakes and other processed foods is linked to several health problems. Excessive sugar consumption can contribute to weight gain, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and tooth decay. While the amounts of individual additives in corn flakes are generally considered safe, long-term consumption of large quantities of certain additives raises concerns about potential long-term effects.
Some studies have suggested possible links between certain artificial colors and hyperactivity in children, though more research is needed. The impact of these additives is often studied in the context of a diet high in processed foods, not just the additive itself. It’s crucial to maintain a balanced diet and limit consumption of highly processed foods like overly sugared corn flakes to minimize potential health risks.
Glycemic Index and Impact on Blood Sugar

Corn flakes, a popular breakfast cereal, have a relatively high glycemic index (GI), meaning they can cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels after consumption. This effect is primarily due to their high carbohydrate content and the processing methods used in their manufacture, which reduce the fiber content and slow the digestion process less than whole grains. Understanding the GI of corn flakes and their impact on blood sugar is crucial for managing blood glucose levels, particularly for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.The glycemic index of corn flakes typically ranges from 70-80, classifying them as a high-GI food.
This high GI value indicates that corn flakes are rapidly digested and absorbed, leading to a swift increase in blood glucose levels. This rapid spike can be problematic for individuals with diabetes, as their bodies may struggle to effectively regulate this sudden influx of glucose, potentially resulting in hyperglycemia. Similarly, individuals with insulin resistance, a condition often preceding type 2 diabetes, may experience amplified blood sugar spikes after consuming high-GI foods like corn flakes due to impaired insulin function.
Corn Flakes and Blood Sugar Management in Diabetes and Insulin Resistance
Consuming high-GI foods like corn flakes regularly can negatively impact long-term blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance. Consistent high blood sugar levels can lead to various complications, including damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs. For example, a person with type 1 diabetes might experience a rapid increase in their blood glucose levels after eating a bowl of corn flakes without sufficient insulin, leading to symptoms like increased thirst, frequent urination, and blurred vision.
Similarly, someone with insulin resistance may find that their blood sugar remains elevated for a longer period after consuming corn flakes, increasing their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Strategies for Mitigating the Glycemic Impact of Corn Flakes
Several strategies can help mitigate the rapid rise in blood sugar levels after consuming corn flakes. One effective approach is to combine corn flakes with foods that have a low glycemic index. Pairing corn flakes with a high-protein food, such as yogurt or nuts, can slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more gradual increase in blood sugar.
Adding a source of healthy fats, like a small amount of nut butter or seeds, can also have a similar effect. For instance, a bowl of corn flakes with a handful of almonds and a dollop of plain yogurt would provide a more balanced nutritional profile and help moderate the blood sugar response compared to corn flakes alone.
Furthermore, choosing corn flakes with added fiber can also help slow down digestion and improve blood sugar control. However, it is crucial to check the nutritional label for actual fiber content as it can vary significantly between brands.
Serving Size and Portion Control

Corn flakes, a popular breakfast cereal, are often consumed in quantities exceeding recommended serving sizes. Understanding appropriate portion sizes and implementing effective portion control strategies are crucial for maintaining a balanced diet and preventing potential health consequences associated with excessive consumption. This section details recommended serving sizes for various demographics and provides practical tips for managing portion control.Appropriate serving sizes of corn flakes vary considerably depending on age, activity level, and overall dietary needs.
Overconsumption can lead to unwanted weight gain, increased sugar intake, and potential nutritional imbalances. Conversely, underconsumption might not provide sufficient energy or essential nutrients.
Recommended Serving Sizes for Different Age Groups and Activity Levels
The recommended serving size for corn flakes is generally indicated on the packaging, typically ranging from 1/2 to 1 cup (depending on the brand and specific product). However, this is just a guideline, and individual needs may vary significantly. Children generally require smaller portions than adults, and active individuals might need slightly more than sedentary individuals. Precise recommendations are best obtained through consultation with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional who can consider individual factors like height, weight, and activity level.
For example, a highly active teenager might require a larger serving than a sedentary adult. A general rule of thumb is to focus on portion sizes that align with the overall daily caloric needs and macro-nutrient targets.
Practical Tips and Strategies for Portion Control When Eating Corn Flakes, Nutrition facts for corn flakes
Implementing effective portion control strategies can significantly impact overall health and well-being. The following strategies can assist in managing corn flake consumption:
- Use a measuring cup: Accurately measure the recommended serving size using a measuring cup to avoid over-pouring.
- Pre-portioning: Measure out individual servings into smaller containers or bags for convenient and controlled portions throughout the week.
- Choose a smaller bowl: Using a smaller bowl can visually reduce the perceived amount of cereal, leading to a smaller consumption.
- Pair with high-fiber foods: Adding fruits, nuts, or seeds to the corn flakes can increase satiety and reduce the overall desire for larger portions.
- Mindful eating: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues. Stop eating when you feel comfortably satisfied, rather than overeating.
Consequences of Consuming Excessive Amounts of Corn Flakes
Regular consumption of excessive amounts of corn flakes can have several negative consequences. These include:
- Weight gain: Corn flakes, particularly those with added sugar, are calorie-dense and can contribute to weight gain if consumed in large quantities.
- Increased sugar intake: Many corn flakes brands contain significant amounts of added sugar, leading to potential health problems like type 2 diabetes and heart disease if consumed excessively.
- Nutritional imbalances: Over-reliance on corn flakes as a primary food source can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber if not part of a balanced diet.
- Digestive issues: Excessive consumption might lead to digestive problems like bloating, gas, or constipation due to high carbohydrate content and low fiber in some varieties.
FAQ Compilation: Nutrition Facts For Corn Flakes
Are corn flakes a good source of fiber?
Corn flakes can provide some fiber, but the amount varies between brands and may be lower than other whole-grain cereals.
Can I eat corn flakes if I have celiac disease?
Most corn flakes are gluten-free, but always check the ingredient label to ensure they are certified gluten-free to avoid cross-contamination.
Are there any corn flakes brands with lower sugar content?
Yes, several brands offer corn flakes with reduced sugar compared to others. Check nutrition labels to compare sugar content per serving.
How can I make corn flakes more nutritious?
Add fruits, nuts, seeds, or yogurt to increase fiber, protein, and micronutrients.